Note
Basic Flopy example
From: Bakker, Mark, Post, Vincent, Langevin, C. D., Hughes, J. D., White, J. T., Starn, J. J. and Fienen, M. N., 2016, Scripting MODFLOW Model Development Using Python and FloPy: Groundwater, v. 54, p. 733–739, https://doi.org/10.1111/gwat.12413.
Import the modflow and utils subpackages of FloPy and give them the aliases fpm and fpu, respectively
[1]:
import os
import sys
import numpy as np
import matplotlib as mpl
# run installed version of flopy or add local path
try:
import flopy
except:
fpth = os.path.abspath(os.path.join("..", "..", ".."))
sys.path.append(fpth)
import flopy
import flopy.modflow as fpm
import flopy.utils as fpu
print(sys.version)
print("numpy version: {}".format(np.__version__))
print("matplotlib version: {}".format(mpl.__version__))
print("flopy version: {}".format(flopy.__version__))
3.10.10 | packaged by conda-forge | (main, Mar 24 2023, 20:08:06) [GCC 11.3.0]
numpy version: 1.24.3
matplotlib version: 3.7.1
flopy version: 3.3.7
Create a MODFLOW model object. Here, the MODFLOW model object is stored in a Python variable called {\tt model}, but this can be an arbitrary name. This object name is important as it will be used as a reference to the model in the remainder of the FloPy script. In addition, a {\tt modelname} is specified when the MODFLOW model object is created. This {\tt modelname} is used for all the files that are created by FloPy for this model.
[2]:
exe = "mf2005"
ws = os.path.join("temp")
model = fpm.Modflow(modelname="gwexample", exe_name=exe, model_ws=ws)
The discretization of the model is specified with the discretization file (DIS) of MODFLOW. The aquifer is divided into 201 cells of length 10 m and width 1 m. The first input of the discretization package is the name of the model object. All other input arguments are self explanatory.
[3]:
fpm.ModflowDis(
model, nlay=1, nrow=1, ncol=201, delr=10, delc=1, top=50, botm=0
)
[3]:
MODFLOW Discretization Package Class.
Parameters
----------
model : model object
The model object (of type :class:`flopy.modflow.Modflow`) to which
this package will be added.
nlay : int
Number of model layers (the default is 1).
nrow : int
Number of model rows (the default is 2).
ncol : int
Number of model columns (the default is 2).
nper : int
Number of model stress periods (the default is 1).
delr : float or array of floats (ncol), optional
An array of spacings along a row (the default is 1.0).
delc : float or array of floats (nrow), optional
An array of spacings along a column (the default is 0.0).
laycbd : int or array of ints (nlay), optional
An array of flags indicating whether or not a layer has a Quasi-3D
confining bed below it. 0 indicates no confining bed, and not zero
indicates a confining bed. LAYCBD for the bottom layer must be 0. (the
default is 0)
top : float or array of floats (nrow, ncol), optional
An array of the top elevation of layer 1. For the common situation in
which the top layer represents a water-table aquifer, it may be
reasonable to set Top equal to land-surface elevation (the default is
1.0)
botm : float or array of floats (nlay, nrow, ncol), optional
An array of the bottom elevation for each model cell (the default is
0.)
perlen : float or array of floats (nper)
An array of the stress period lengths.
nstp : int or array of ints (nper)
Number of time steps in each stress period (default is 1).
tsmult : float or array of floats (nper)
Time step multiplier (default is 1.0).
steady : bool or array of bool (nper)
true or False indicating whether or not stress period is steady state
(default is True).
itmuni : int
Time units, default is days (4)
lenuni : int
Length units, default is meters (2)
extension : string
Filename extension (default is 'dis')
unitnumber : int
File unit number (default is None).
filenames : str or list of str
Filenames to use for the package. If filenames=None the package name
will be created using the model name and package extension. If a
single string is passed the package will be set to the string.
Default is None.
xul : float
x coordinate of upper left corner of the grid, default is None, which
means xul will be set to zero.
yul : float
y coordinate of upper-left corner of the grid, default is None, which
means yul will be calculated as the sum of the delc array. This
default, combined with the xul and rotation defaults will place the
lower-left corner of the grid at (0, 0).
rotation : float
counter-clockwise rotation (in degrees) of the grid about the lower-
left corner. default is 0.0
crs : pyproj.CRS, optional if `prjfile` is specified
Coordinate reference system (CRS) for the model grid
(must be projected; geographic CRS are not supported).
The value can be anything accepted by
:meth:`pyproj.CRS.from_user_input() <pyproj.crs.CRS.from_user_input>`,
such as an authority string (eg "EPSG:26916") or a WKT string.
prjfile : str or pathlike, optional if `crs` is specified
ESRI-style projection file with well-known text defining the CRS
for the model grid (must be projected; geographic CRS are not supported).
start_datetime : str
starting datetime of the simulation. default is '1/1/1970'
Attributes
----------
heading : str
Text string written to top of package input file.
Methods
-------
See Also
--------
Notes
-----
Examples
--------
>>> import flopy
>>> m = flopy.modflow.Modflow()
>>> dis = flopy.modflow.ModflowDis(m)
_name = DIS
_parent = MODFLOW 1 layer(s) 1 row(s) 201 column(s) 1 stress period(s) ('flopy.modflow.mf.Modflow)
_totim = None ('NoneType)
acceptable_dtypes (list, items = 3)
allowDuplicates = False ('bool)
botm = <flopy.utils.util_array.Util3d object at 0x7faee7f05c00> ('flopy.utils.util_array.Util3d)
delc = <flopy.utils.util_array.Util2d object at 0x7faee7f05900> ('flopy.utils.util_array.Util2d)
delr = <flopy.utils.util_array.Util2d object at 0x7faee7f042b0> ('flopy.utils.util_array.Util2d)
file_name = gwexample.dis
fn_path = /home/runner/work/flopy/flopy/.docs/groundwater_paper/Notebooks/temp/gwexample.dis ('str)
itmuni = 4 ('int)
itmuni_dict = {0: 'undefined', 1: 'seconds', 2: 'minutes', 3: 'hours', 4: 'days', 5: 'years'} ('dict)
laycbd = <flopy.utils.util_array.Util2d object at 0x7faee7f061a0> ('flopy.utils.util_array.Util2d)
lenuni = 2 ('int)
ncol = 201 ('int)
nlay = 1 ('int)
nper = 1 ('int)
nrow = 1 ('int)
nstp = <flopy.utils.util_array.Util2d object at 0x7faee7f05ba0> ('flopy.utils.util_array.Util2d)
perlen = <flopy.utils.util_array.Util2d object at 0x7faee7f05b10> ('flopy.utils.util_array.Util2d)
start_datetime = 1-1-1970 ('str)
steady = <flopy.utils.util_array.Util2d object at 0x7faee7f06f20> ('flopy.utils.util_array.Util2d)
top = <flopy.utils.util_array.Util2d object at 0x7faee7f05c60> ('flopy.utils.util_array.Util2d)
tr = <flopy.utils.reference.TemporalReference object at 0x7faee7f07280> ('flopy.utils.reference.TemporalReference)
tsmult = <flopy.utils.util_array.Util2d object at 0x7faee7f05ed0> ('flopy.utils.util_array.Util2d)
unit_number = 11
Active cells and the like are defined with the Basic package (BAS), which is required for every MODFLOW model. It contains the {\tt ibound} array, which is used to specify which cells are active (value is positive), inactive (value is 0), or fixed head (value is negative). The {\tt numpy} package (aliased as {\tt np}) can be used to quickly initialize the {\tt ibound} array with values of 1, and then set the {\tt ibound} value for the first and last columns to -1. The {\tt numpy} package (and Python, in general) uses zero-based indexing and supports negative indexing so that row 1 and column 1, and row 1 and column 201, can be referenced as [0, 0], and [0, -1], respectively. Although this simulation is for steady flow, starting heads still need to be specified. They are used as the head for fixed-head cells (where {\tt ibound} is negative), and as a starting point to compute the saturated thickness for cases of unconfined flow.
[4]:
ibound = np.ones((1, 201))
ibound[0, 0] = ibound[0, -1] = -1
fpm.ModflowBas(model, ibound=ibound, strt=20)
[4]:
MODFLOW Basic Package Class.
Parameters
----------
model : model object
The model object (of type :class:`flopy.modflow.mf.Modflow`) to which
this package will be added.
ibound : array of ints, optional
The ibound array (the default is 1).
strt : array of floats, optional
An array of starting heads (the default is 1.0).
ifrefm : bool, optional
Indication if data should be read using free format (the default is
True).
ixsec : bool, optional
Indication of whether model is cross sectional or not (the default is
False).
ichflg : bool, optional
Flag indicating that flows between constant head cells should be
calculated (the default is False).
stoper : float
percent discrepancy that is compared to the budget percent discrepancy
continue when the solver convergence criteria are not met. Execution
will unless the budget percent discrepancy is greater than stoper
(default is None). MODFLOW-2005 only
hnoflo : float
Head value assigned to inactive cells (default is -999.99).
extension : str, optional
File extension (default is 'bas').
unitnumber : int, optional
FORTRAN unit number for this package (default is None).
filenames : str or list of str
Filenames to use for the package. If filenames=None the package name
will be created using the model name and package extension. If a single
string is passed the package name will be set to the string.
Default is None.
Attributes
----------
heading : str
Text string written to top of package input file.
options : list of str
Can be either or a combination of XSECTION, CHTOCH or FREE.
ifrefm : bool
Indicates whether or not packages will be written as free format.
Methods
-------
See Also
--------
Notes
-----
Examples
--------
>>> import flopy
>>> m = flopy.modflow.Modflow()
>>> bas = flopy.modflow.ModflowBas(m)
_name = BAS6
_parent = MODFLOW 1 layer(s) 1 row(s) 201 column(s) 1 stress period(s) ('flopy.modflow.mf.Modflow)
acceptable_dtypes (list, items = 3)
allowDuplicates = False ('bool)
file_name = gwexample.bas
fn_path = /home/runner/work/flopy/flopy/.docs/groundwater_paper/Notebooks/temp/gwexample.bas ('str)
hnoflo = -999.99 ('float)
ibound = <flopy.utils.util_array.Util3d object at 0x7faee7f06b00> ('flopy.utils.util_array.Util3d)
ichflg = False ('bool)
ixsec = False ('bool)
options = ('str)
stoper = None ('NoneType)
strt = <flopy.utils.util_array.Util3d object at 0x7faeae654e50> ('flopy.utils.util_array.Util3d)
unit_number = 13
The hydraulic properties of the aquifer are specified with the Layer Properties Flow (LPF) package (alternatively, the Block Centered Flow (BCF) package may be used). Only the hydraulic conductivity of the aquifer and the layer type ({\tt laytyp}) need to be specified. The latter is set to 1, which means that MODFLOW will calculate the saturated thickness differently depending on whether or not the head is above the top of the aquifer.
[5]:
fpm.ModflowLpf(model, hk=10, laytyp=1)
[5]:
MODFLOW Layer Property Flow Package Class.
Parameters
----------
model : model object
The model object (of type :class:`flopy.modflow.mf.Modflow`) to which
this package will be added.
ipakcb : int
A flag that is used to determine if cell-by-cell budget data should be
saved. If ipakcb is non-zero cell-by-cell budget data will be saved.
(default is 0)
hdry : float
Is the head that is assigned to cells that are converted to dry during
a simulation. Although this value plays no role in the model
calculations, it is useful as an indicator when looking at the
resulting heads that are output from the model. HDRY is thus similar
to HNOFLO in the Basic Package, which is the value assigned to cells
that are no-flow cells at the start of a model simulation.
(default is -1.e30).
laytyp : int or array of ints (nlay)
Layer type, contains a flag for each layer that specifies the layer
type.
0 confined
>0 convertible
<0 convertible unless the THICKSTRT option is in effect.
(default is 0).
layavg : int or array of ints (nlay)
Layer average
0 is harmonic mean
1 is logarithmic mean
2 is arithmetic mean of saturated thickness and logarithmic mean of
of hydraulic conductivity
(default is 0).
chani : float or array of floats (nlay)
contains a value for each layer that is a flag or the horizontal
anisotropy. If CHANI is less than or equal to 0, then variable HANI
defines horizontal anisotropy. If CHANI is greater than 0, then CHANI
is the horizontal anisotropy for the entire layer, and HANI is not
read. If any HANI parameters are used, CHANI for all layers must be
less than or equal to 0. Use as many records as needed to enter a
value of CHANI for each layer. The horizontal anisotropy is the ratio
of the hydraulic conductivity along columns (the Y direction) to the
hydraulic conductivity along rows (the X direction).
(default is 1).
layvka : int or array of ints (nlay)
a flag for each layer that indicates whether variable VKA is vertical
hydraulic conductivity or the ratio of horizontal to vertical
hydraulic conductivity.
0: VKA is vertical hydraulic conductivity
not 0: VKA is the ratio of horizontal to vertical hydraulic conductivity
(default is 0).
laywet : int or array of ints (nlay)
contains a flag for each layer that indicates if wetting is active.
0 wetting is inactive
not 0 wetting is active
(default is 0).
wetfct : float
is a factor that is included in the calculation of the head that is
initially established at a cell when it is converted from dry to wet.
(default is 0.1).
iwetit : int
is the iteration interval for attempting to wet cells. Wetting is
attempted every IWETIT iteration. If using the PCG solver
(Hill, 1990), this applies to outer iterations, not inner iterations.
If IWETIT less than or equal to 0, it is changed to 1.
(default is 1).
ihdwet : int
is a flag that determines which equation is used to define the
initial head at cells that become wet.
(default is 0)
hk : float or array of floats (nlay, nrow, ncol)
is the hydraulic conductivity along rows. HK is multiplied by
horizontal anisotropy (see CHANI and HANI) to obtain hydraulic
conductivity along columns.
(default is 1.0).
hani : float or array of floats (nlay, nrow, ncol)
is the ratio of hydraulic conductivity along columns to hydraulic
conductivity along rows, where HK of item 10 specifies the hydraulic
conductivity along rows. Thus, the hydraulic conductivity along
columns is the product of the values in HK and HANI.
(default is 1.0).
vka : float or array of floats (nlay, nrow, ncol)
is either vertical hydraulic conductivity or the ratio of horizontal
to vertical hydraulic conductivity depending on the value of LAYVKA.
(default is 1.0).
ss : float or array of floats (nlay, nrow, ncol)
is specific storage unless the STORAGECOEFFICIENT option is used.
When STORAGECOEFFICIENT is used, Ss is confined storage coefficient.
(default is 1.e-5).
sy : float or array of floats (nlay, nrow, ncol)
is specific yield.
(default is 0.15).
vkcb : float or array of floats (nlay, nrow, ncol)
is the vertical hydraulic conductivity of a Quasi-three-dimensional
confining bed below a layer. (default is 0.0). Note that if an array
is passed for vkcb it must be of size (nlay, nrow, ncol) even though
the information for the bottom layer is not needed.
wetdry : float or array of floats (nlay, nrow, ncol)
is a combination of the wetting threshold and a flag to indicate
which neighboring cells can cause a cell to become wet.
(default is -0.01).
storagecoefficient : boolean
indicates that variable Ss and SS parameters are read as storage
coefficient rather than specific storage.
(default is False).
constantcv : boolean
indicates that vertical conductance for an unconfined cell is
computed from the cell thickness rather than the saturated thickness.
The CONSTANTCV option automatically invokes the NOCVCORRECTION
option. (default is False).
thickstrt : boolean
indicates that layers having a negative LAYTYP are confined, and their
cell thickness for conductance calculations will be computed as
STRT-BOT rather than TOP-BOT. (default is False).
nocvcorrection : boolean
indicates that vertical conductance is not corrected when the vertical
flow correction is applied. (default is False).
novfc : boolean
turns off the vertical flow correction under dewatered conditions.
This option turns off the vertical flow calculation described on p.
5-8 of USGS Techniques and Methods Report 6-A16 and the vertical
conductance correction described on p. 5-18 of that report.
(default is False).
extension : string
Filename extension (default is 'lpf')
unitnumber : int
File unit number (default is None).
filenames : str or list of str
Filenames to use for the package and the output files. If
filenames=None the package name will be created using the model name
and package extension and the cbc output name will be created using
the model name and .cbc extension (for example, modflowtest.cbc),
if ipakcbc is a number greater than zero. If a single string is passed
the package will be set to the string and cbc output name will be
created using the model name and .cbc extension, if ipakcbc is a
number greater than zero. To define the names for all package files
(input and output) the length of the list of strings should be 2.
Default is None.
add_package : bool
Flag to add the initialised package object to the parent model object.
Default is True.
Attributes
----------
Methods
-------
See Also
--------
Notes
-----
Examples
--------
>>> import flopy
>>> m = flopy.modflow.Modflow()
>>> lpf = flopy.modflow.ModflowLpf(m)
_name = LPF
_parent = MODFLOW 1 layer(s) 1 row(s) 201 column(s) 1 stress period(s) ('flopy.modflow.mf.Modflow)
acceptable_dtypes (list, items = 3)
allowDuplicates = False ('bool)
chani = <flopy.utils.util_array.Util2d object at 0x7faee7ee21d0> ('flopy.utils.util_array.Util2d)
file_name = gwexample.lpf
fn_path = /home/runner/work/flopy/flopy/.docs/groundwater_paper/Notebooks/temp/gwexample.lpf ('str)
hani = <flopy.utils.util_array.Util3d object at 0x7faee7ee39d0> ('flopy.utils.util_array.Util3d)
hdry = -1e+30 ('float)
hk = <flopy.utils.util_array.Util3d object at 0x7faee7ee26b0> ('flopy.utils.util_array.Util3d)
ihdwet = 0 ('int)
ikcflag = 0 ('int)
ipakcb = 0 ('int)
iwetit = 1 ('int)
layavg = <flopy.utils.util_array.Util2d object at 0x7faee7ee3250> ('flopy.utils.util_array.Util2d)
laytyp = <flopy.utils.util_array.Util2d object at 0x7faee7f04340> ('flopy.utils.util_array.Util2d)
layvka = <flopy.utils.util_array.Util2d object at 0x7faee7ee1f90> ('flopy.utils.util_array.Util2d)
laywet = <flopy.utils.util_array.Util2d object at 0x7faee7ee1ff0> ('flopy.utils.util_array.Util2d)
nplpf = 0 ('int)
options = ('str)
ss = <flopy.utils.util_array.Util3d object at 0x7faeae654eb0> ('flopy.utils.util_array.Util3d)
sy = <flopy.utils.util_array.Util3d object at 0x7faeae654c10> ('flopy.utils.util_array.Util3d)
unit_number = 15
vka = <flopy.utils.util_array.Util3d object at 0x7faeae654d30> ('flopy.utils.util_array.Util3d)
vkcb = <flopy.utils.util_array.Util3d object at 0x7faeae654b20> ('flopy.utils.util_array.Util3d)
wetdry = <flopy.utils.util_array.Util3d object at 0x7faeae654a90> ('flopy.utils.util_array.Util3d)
wetfct = 0.1 ('float)
Aquifer recharge is simulated with the Recharge package (RCH) and the extraction of water at the two ditches is simulated with the Well package (WEL). The latter requires specification of the layer, row, column, and injection rate of the well for each stress period. The layers, rows, columns, and the stress period are numbered (consistent with Python’s zero-based numbering convention) starting at 0. The required data are stored in a Python dictionary ({\tt lrcQ} in the code below), which is used in FloPy to store data that can vary by stress period. The {\tt lrcQ} dictionary specifies that two wells (one in cell 1, 1, 51 and one in cell 1, 1, 151), each with a rate of -1 m\(^3\)/m/d, will be active for the first stress period. Because this is a steady-state model, there is only one stress period and therefore only one entry in the dictionary.
[6]:
fpm.ModflowRch(model, rech=0.001)
lrcQ = {0: [[0, 0, 50, -1], [0, 0, 150, -1]]}
fpm.ModflowWel(model, stress_period_data=lrcQ)
[6]:
MODFLOW Well Package Class.
Parameters
----------
model : model object
The model object (of type :class:`flopy.modflow.mf.Modflow`) to which
this package will be added.
ipakcb : int
A flag that is used to determine if cell-by-cell budget data should be
saved. If ipakcb is non-zero cell-by-cell budget data will be saved.
(default is 0).
stress_period_data : list of boundaries, or recarray of boundaries, or
dictionary of boundaries
Each well is defined through definition of
layer (int), row (int), column (int), flux (float).
The simplest form is a dictionary with a lists of boundaries for each
stress period, where each list of boundaries itself is a list of
boundaries. Indices of the dictionary are the numbers of the stress
period. This gives the form of:
stress_period_data =
{0: [
[lay, row, col, flux],
[lay, row, col, flux],
[lay, row, col, flux]
],
1: [
[lay, row, col, flux],
[lay, row, col, flux],
[lay, row, col, flux]
], ...
kper:
[
[lay, row, col, flux],
[lay, row, col, flux],
[lay, row, col, flux]
]
}
Note that if the number of lists is smaller than the number of stress
periods, then the last list of wells will apply until the end of the
simulation. Full details of all options to specify stress_period_data
can be found in the flopy3 boundaries Notebook in the basic
subdirectory of the examples directory
dtype : custom datatype of stress_period_data.
If None the default well datatype will be applied (default is None).
extension : string
Filename extension (default is 'wel')
options : list of strings
Package options (default is None).
unitnumber : int
File unit number (default is None).
filenames : str or list of str
Filenames to use for the package and the output files. If
filenames=None the package name will be created using the model name
and package extension and the cbc output name will be created using
the model name and .cbc extension (for example, modflowtest.cbc),
if ipakcbc is a number greater than zero. If a single string is passed
the package will be set to the string and cbc output names will be
created using the model name and .cbc extension, if ipakcbc is a
number greater than zero. To define the names for all package files
(input and output) the length of the list of strings should be 2.
Default is None.
add_package : bool
Flag to add the initialised package object to the parent model object.
Default is True.
Attributes
----------
mxactw : int
Maximum number of wells for a stress period. This is calculated
automatically by FloPy based on the information in
stress_period_data.
Methods
-------
See Also
--------
Notes
-----
Parameters are not supported in FloPy.
Examples
--------
>>> import flopy
>>> m = flopy.modflow.Modflow()
>>> lrcq = {0:[[2, 3, 4, -100.]], 1:[[2, 3, 4, -100.]]}
>>> wel = flopy.modflow.ModflowWel(m, stress_period_data=lrcq)
_name = WEL
_parent = MODFLOW 1 layer(s) 1 row(s) 201 column(s) 1 stress period(s) ('flopy.modflow.mf.Modflow)
acceptable_dtypes (list, items = 3)
allowDuplicates = False ('bool)
dtype = [('k', '<i8'), ('i', '<i8'), ('j', '<i8'), ('flux', '<f4')] ('numpy.dtype[void])
file_name = gwexample.wel
fn_path = /home/runner/work/flopy/flopy/.docs/groundwater_paper/Notebooks/temp/gwexample.wel ('str)
ipakcb = 0 ('int)
iunitramp = None ('NoneType)
np = 0 ('int)
options (list, items = 0)
phiramp = None ('NoneType)
specify = False ('bool)
stress_period_data = <flopy.utils.util_list.MfList object at 0x7faeae655870> ('flopy.utils.util_list.MfList)
unit_number = 20
The Preconditioned Conjugate-Gradient (PCG) solver, using the default settings, is specified to solve the model.
[7]:
fpm.ModflowPcg(model)
[7]:
MODFLOW Pcg Package Class.
Parameters
----------
model : model object
The model object (of type :class:`flopy.modflow.mf.Modflow`) to which
this package will be added.
mxiter : int
maximum number of outer iterations. (default is 50)
iter1 : int
maximum number of inner iterations. (default is 30)
npcond : int
flag used to select the matrix conditioning method. (default is 1).
specify npcond = 1 for Modified Incomplete Cholesky.
specify npcond = 2 for Polynomial.
hclose : float
is the head change criterion for convergence. (default is 1e-5).
rclose : float
is the residual criterion for convergence. (default is 1e-5)
relax : float
is the relaxation parameter used with npcond = 1. (default is 1.0)
nbpol : int
is only used when npcond = 2 to indicate whether the estimate of the
upper bound on the maximum eigenvalue is 2.0, or whether the estimate
will be calculated. nbpol = 2 is used to specify the value is 2.0;
for any other value of nbpol, the estimate is calculated. Convergence
is generally insensitive to this parameter. (default is 0).
iprpcg : int
solver print out interval. (default is 0).
mutpcg : int
If mutpcg = 0, tables of maximum head change and residual will be
printed each iteration.
If mutpcg = 1, only the total number of iterations will be printed.
If mutpcg = 2, no information will be printed.
If mutpcg = 3, information will only be printed if convergence fails.
(default is 3).
damp : float
is the steady-state damping factor. (default is 1.)
dampt : float
is the transient damping factor. (default is 1.)
ihcofadd : int
is a flag that determines what happens to an active cell that is
surrounded by dry cells. (default is 0). If ihcofadd=0, cell
converts to dry regardless of HCOF value. This is the default, which
is the way PCG2 worked prior to the addition of this option. If
ihcofadd<>0, cell converts to dry only if HCOF has no head-dependent
stresses or storage terms.
extension : list string
Filename extension (default is 'pcg')
unitnumber : int
File unit number (default is None).
filenames : str or list of str
Filenames to use for the package. If filenames=None the package name
will be created using the model name and package extension. If a
single string is passed the package will be set to the string.
Default is None.
Attributes
----------
Methods
-------
See Also
--------
Notes
-----
Examples
--------
>>> import flopy
>>> m = flopy.modflow.Modflow()
>>> pcg = flopy.modflow.ModflowPcg(m)
_name = PCG
_parent = MODFLOW 1 layer(s) 1 row(s) 201 column(s) 1 stress period(s) ('flopy.modflow.mf.Modflow)
acceptable_dtypes (list, items = 3)
allowDuplicates = False ('bool)
damp = 1.0 ('float)
dampt = 1.0 ('float)
file_name = gwexample.pcg
fn_path = /home/runner/work/flopy/flopy/.docs/groundwater_paper/Notebooks/temp/gwexample.pcg ('str)
hclose = 1e-05 ('float)
ihcofadd = 0 ('int)
iprpcg = 0 ('int)
iter1 = 30 ('int)
mutpcg = 3 ('int)
mxiter = 50 ('int)
nbpol = 0 ('int)
npcond = 1 ('int)
rclose = 1e-05 ('float)
relax = 1.0 ('float)
unit_number = 27
The frequency and type of output that MODFLOW writes to an output file is specified with the Output Control (OC) package. In this case, the budget is printed and heads are saved (the default), so no arguments are needed.
[8]:
fpm.ModflowOc(model)
[8]:
MODFLOW Output Control Package Class.
Parameters
----------
model : model object
The model object (of type :class:`flopy.modflow.mf.Modflow`) to which
this package will be added.
ihedfm : int
is a code for the format in which heads will be printed.
(default is 0).
iddnfm : int
is a code for the format in which drawdown will be printed.
(default is 0).
chedfm : string
is a character value that specifies the format for saving heads.
The format must contain 20 characters or less and must be a valid
Fortran format that is enclosed in parentheses. The format must be
enclosed in apostrophes if it contains one or more blanks or commas.
The optional word LABEL after the format is used to indicate that
each layer of output should be preceded with a line that defines the
output (simulation time, the layer being output, and so forth). If
there is no record specifying CHEDFM, then heads are written to a
binary (unformatted) file. Binary files are usually more compact than
text files, but they are not generally transportable among different
computer operating systems or different Fortran compilers.
(default is None)
cddnfm : string
is a character value that specifies the format for saving drawdown.
The format must contain 20 characters or less and must be a valid
Fortran format that is enclosed in parentheses. The format must be
enclosed in apostrophes if it contains one or more blanks or commas.
The optional word LABEL after the format is used to indicate that
each layer of output should be preceded with a line that defines the
output (simulation time, the layer being output, and so forth). If
there is no record specifying CDDNFM, then drawdowns are written to a
binary (unformatted) file. Binary files are usually more compact than
text files, but they are not generally transportable among different
computer operating systems or different Fortran compilers.
(default is None)
cboufm : string
is a character value that specifies the format for saving ibound.
The format must contain 20 characters or less and must be a valid
Fortran format that is enclosed in parentheses. The format must be
enclosed in apostrophes if it contains one or more blanks or commas.
The optional word LABEL after the format is used to indicate that
each layer of output should be preceded with a line that defines the
output (simulation time, the layer being output, and so forth). If
there is no record specifying CBOUFM, then ibounds are written to a
binary (unformatted) file. Binary files are usually more compact than
text files, but they are not generally transportable among different
computer operating systems or different Fortran compilers.
(default is None)
stress_period_data : dictionary of lists
Dictionary key is a tuple with the zero-based period and step
(IPEROC, ITSOC) for each print/save option list. If stress_period_data
is None, then heads are saved for the last time step of each stress
period. (default is None)
The list can have any valid MODFLOW OC print/save option:
PRINT HEAD
PRINT DRAWDOWN
PRINT BUDGET
SAVE HEAD
SAVE DRAWDOWN
SAVE BUDGET
SAVE IBOUND
The lists can also include (1) DDREFERENCE in the list to reset
drawdown reference to the period and step and (2) a list of layers
for PRINT HEAD, SAVE HEAD, PRINT DRAWDOWN, SAVE DRAWDOWN, and
SAVE IBOUND.
stress_period_data = {(0,1):['save head']}) would save the head for
the second timestep in the first stress period.
compact : boolean
Save results in compact budget form. (default is True).
extension : list of strings
(default is ['oc', 'hds', 'ddn', 'cbc', 'ibo']).
unitnumber : list of ints
(default is [14, 51, 52, 53, 0]).
filenames : str or list of str
Filenames to use for the package and the head, drawdown, budget (not
used), and ibound output files. If filenames=None the package name
will be created using the model name and package extension and the
output file names will be created using the model name and extensions.
If a single string is passed the package will be set to the string and
output names will be created using the model name and head, drawdown,
budget, and ibound extensions. To define the names for all package
files (input and output) the length of the list of strings should be 5.
Default is None.
Attributes
----------
Methods
-------
See Also
--------
Notes
-----
The "words" method for specifying output control is the only option
available. Also, the "compact" budget should normally be used as it
produces files that are typically much smaller. The compact budget form is
also a requirement for using the MODPATH particle tracking program.
Examples
--------
>>> import flopy
>>> m = flopy.modflow.Modflow()
>>> spd = {(0, 0): ['print head'],
... (0, 1): [],
... (0, 249): ['print head'],
... (0, 250): [],
... (0, 499): ['print head', 'save ibound'],
... (0, 500): [],
... (0, 749): ['print head', 'ddreference'],
... (0, 750): [],
... (0, 999): ['print head']}
>>> oc = flopy.modflow.ModflowOc(m, stress_period_data=spd, cboufm='(20i5)')
_name = OC
_parent = MODFLOW 1 layer(s) 1 row(s) 201 column(s) 1 stress period(s) ('flopy.modflow.mf.Modflow)
acceptable_dtypes (list, items = 3)
allowDuplicates = False ('bool)
cboufm = None ('NoneType)
cddnfm = None ('NoneType)
chedfm = None ('NoneType)
compact = True ('bool)
file_name = gwexample.oc
fn_path = /home/runner/work/flopy/flopy/.docs/groundwater_paper/Notebooks/temp/gwexample.oc ('str)
ibouun = 0 ('int)
iddnfm = 0 ('int)
ihedfm = 0 ('int)
iubud = 0 ('int)
iuddn = 0 ('int)
iuhead = 51 ('int)
iuibnd = 0 ('int)
label = LABEL ('str)
savebud = False ('bool)
saveddn = False ('bool)
savehead = True ('bool)
saveibnd = False ('bool)
stress_period_data = {(0, 0): ['save head']} ('dict)
unit_number = 14
Finally the MODFLOW input files are written (eight files for this model) and the model is run. This requires, of course, that MODFLOW is installed on your computer and FloPy can find the executable in your path.
[9]:
model.write_input()
success, buff = model.run_model(silent=True, report=True)
if success:
for line in buff:
print(line)
else:
raise ValueError("Failed to run.")
MODFLOW-2005
U.S. GEOLOGICAL SURVEY MODULAR FINITE-DIFFERENCE GROUND-WATER FLOW MODEL
Version 1.12.00 2/3/2017
Using NAME file: gwexample.nam
Run start date and time (yyyy/mm/dd hh:mm:ss): 2023/05/04 16:16:03
Solving: Stress period: 1 Time step: 1 Ground-Water Flow Eqn.
Run end date and time (yyyy/mm/dd hh:mm:ss): 2023/05/04 16:16:03
Elapsed run time: 0.001 Seconds
Normal termination of simulation
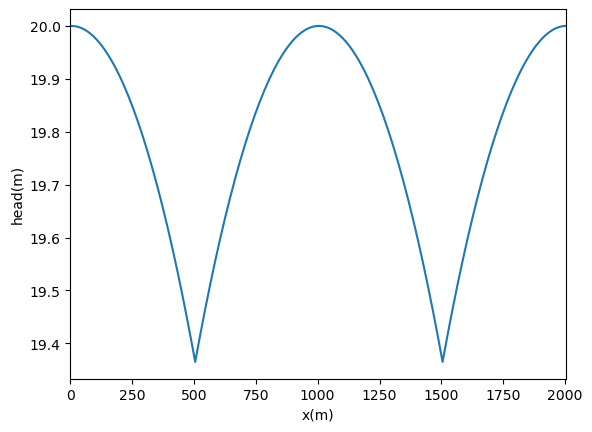
After MODFLOW has responded with the positive {\tt Normal termination of simulation}, the calculated heads can be read from the binary output file. First a file object is created. As the modelname used for all MODFLOW files was specified as {\tt gwexample} in step 1, the file with the heads is called {\tt gwexample.hds}. FloPy includes functions to read data from the file object, including heads for specified layers or time steps, or head time series at individual cells. For this simple mode, all computed heads are read.
[10]:
fpth = os.path.join(ws, "gwexample.hds")
hfile = fpu.HeadFile(fpth)
h = hfile.get_data(totim=1.0)
The heads are now stored in the Python variable {\tt h}. FloPy includes powerful plotting functions to plot the grid, boundary conditions, head, etc. This functionality is demonstrated later. For this simple one-dimensional example, a plot is created with the matplotlib package
[11]:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
ax = plt.subplot(111)
x = model.modelgrid.xcellcenters[0]
ax.plot(x, h[0, 0, :])
ax.set_xlim(0, x.max())
ax.set_xlabel("x(m)")
ax.set_ylabel("head(m)")
plt.show()
[ ]: